(+86)-137 5851 1881
(+86)-137 5851 1881
Detailed Explanation of Slack Adjuster Types
Content
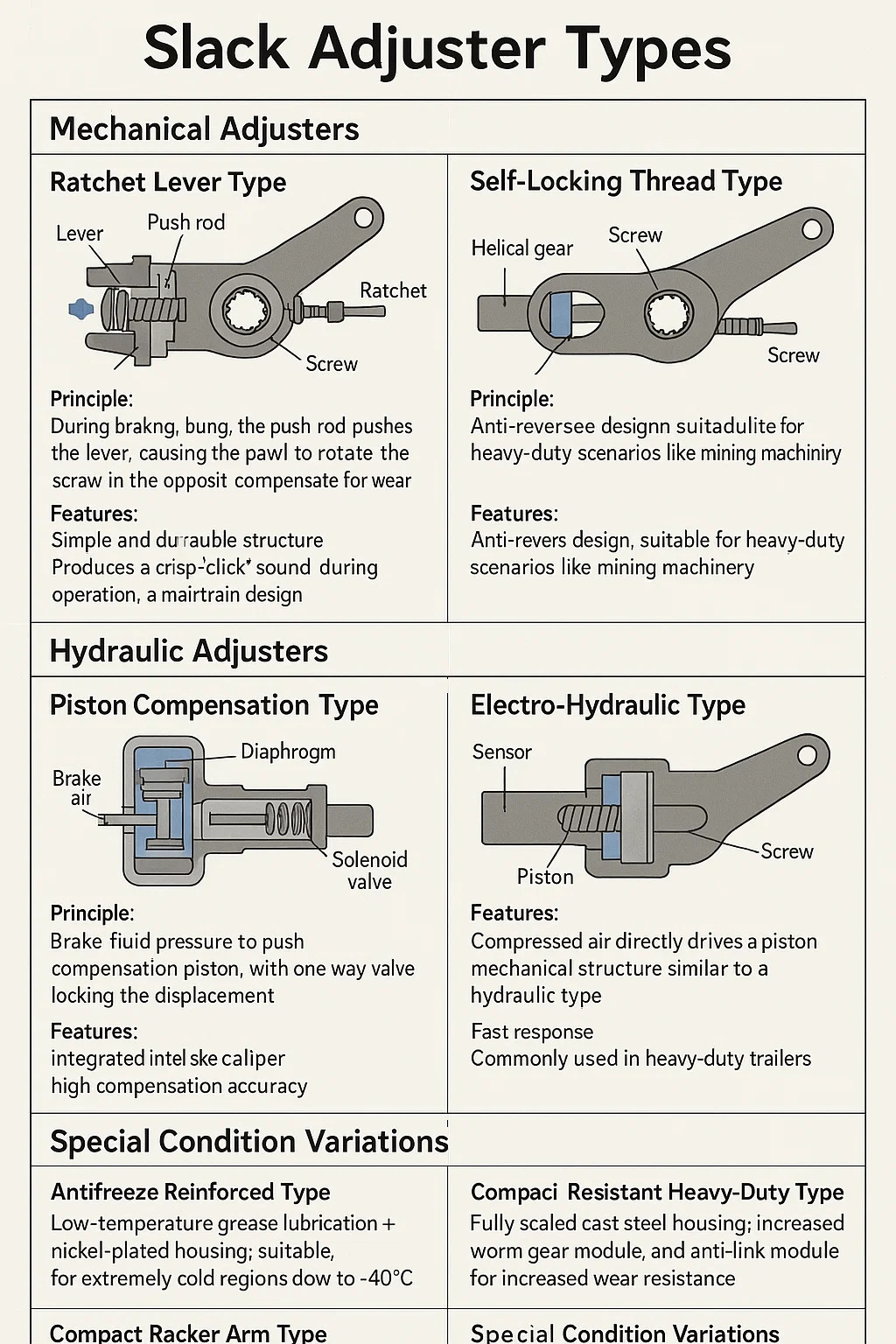
Principle: During braking, the push rod pushes the lever, causing the pawl to rotate the ratchet, resulting in a slight extension of the screw to compensate for wear slack.
Features: Simple and durable structure, produces a crisp "click" sound during operation, a mainstream design for trucks.
Principle: The helical gear clutch at the end of the push rod engages the moment the brake is released, rotating the screw in the opposite direction to achieve compensation.
Features: Anti-reverse design, suitable for heavy-duty scenarios such as mining machinery.
Principle: Utilizes brake fluid pressure to push the compensation piston, with a one-way valve locking the displacement.
Features: Integrated into the brake caliper, high compensation accuracy, commonly used in passenger cars/precision equipment.
Principle: Sensors monitor the slack, and the ECU controls a solenoid valve to drive the compensation cylinder.
Features: Strong self-adaptability, standard equipment in new energy vehicles, requires matching with the vehicle's overall control system.
Principle: Brake air pressure deforms a rubber diaphragm, which in turn rotates a screw via a ratchet mechanism.
Features: Resistant to mud and water corrosion; standard configuration for commercial air-brake vehicles.
Principle: Compressed air directly drives a piston; mechanical structure similar to a hydraulic type.
Features: Fast response; commonly used in heavy-duty trailers.
Features: Low-temperature grease lubrication + nickel-plated housing; suitable for extremely cold regions down to -40℃.
Features: Fully sealed cast steel housing; increased worm gear module and anti-link module for increased wear resistance.
Features: External rocker arm for direction switching; suitable for space-constrained engineering applications and construction machinery.
| Type | Recommended Applications | Avoid In |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Ratchet | Highway trucks & coaches | Equipment with high-pressure washing |
| Hydraulic Piston | Passenger vehicles & machine tools | High-dust mining sites |
| Pneumatic Diaphragm | Freight trailers & city buses | Loaders with frequent reversing |
| Electro-Hydraulic | EVs & smart driving systems | Older vehicles without ECU support |