(+86)-137 5851 1881
(+86)-137 5851 1881
Analysis of the Core Types of Automatic Slack Adjusters
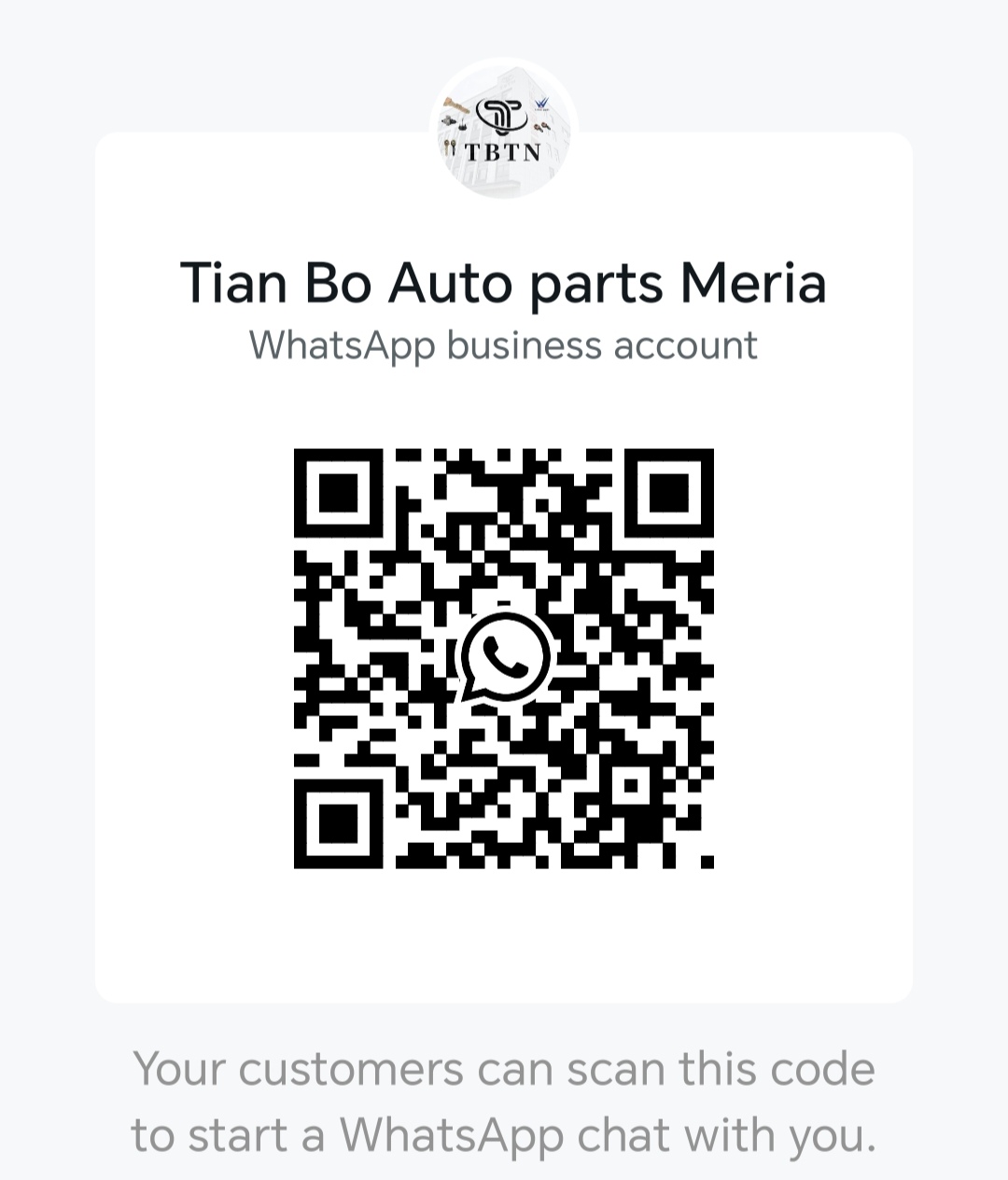
1. Classification by Power Transmission Method
--Mechanical
Ratchet Lever Type: During braking, a lever pushes a pawl, driving the ratchet to rotate unidirectionally, extending a screw to compensate for clearance (a mainstream design for trucks).
Self-locking Thread Type: A helical gear clutch is installed at the end of the push rod. When the brake is released, the lever engages in reverse, causing the screw to rotate slightly to compensate for clearance (commonly used in heavy-duty machinery).
--Hydraulic
Piston Compensation Type: Utilizes brake fluid pressure to push a compensating piston, compressing a one-way valve to retain displacement (integrated into the caliper brake cylinder).
Gap Sensing Type: A solenoid valve is triggered by oil pressure differentials to control the movement of the compensating cylinder (a braking system for precision machine tools).
--Pneumatic
Diaphragm Adjustment Type: Brake air pressure deforms the diaphragm, triggering a ratchet mechanism to rotate the screw (standard for pneumatic brakes on commercial vehicles).
2. Classification by Gap Detection Mechanism
--Stroke Trigger Type: Monitors the stroke of the brake chamber push rod/hydraulic piston and initiates compensation if the stroke exceeds the limit (fast response, mainstream application).
--Wear Accumulation Type
An internal counter records the number of braking cycles and automatically compensates after a preset threshold (earlier mechanical structures are prone to error and hysteresis).
--Real-Time Feedback Type
A Hall effect sensor monitors the push rod position, and the electronic control unit dynamically corrects it (intelligent braking system for new energy vehicles).
3. Classification by Structural Layout
--Angle Drive Type
The adjuster axis is arranged at 90 degrees to the brake camshaft, and torque is transmitted via a worm gear (traditional S-cam brake).
--Coaxial Direct Push Type
The push rod is coaxial with the brake chamber piston, directly transmitting thrust (integrated disc brake solution).
--Side Rocker Arm Type
Motion direction is changed by an external rocker arm, allowing for adaptation to confined spaces (swing brakes for construction machinery).
4. Special Purpose Variants
--Anti-Freeze and Ice-Breaking Type
The screw seal chamber is injected with low-temperature grease, and the housing is nickel-plated for anti-icing (specially for mining trucks in polar regions).
--Fouling-Resistant Heavy-Duty Type
Fully enclosed cast steel housing with a 40% increased worm module (for muck trucks and mining dump trucks). Dual-redundant electronic control: Two motors and sensors provide backup for each other, automatically switching in the event of a failure (core module for high-speed rail braking).
| Classification Basis | Type | Key Mechanism | Typical Application | Failure Risk |
| By Actuation Method | Mechanical Ratchet | Lever-driven pawl rotates ratchet wheel to extend screw rod | Heavy-duty trucks | Pawl spring fracture in dusty env. |
| Mechanical Non-Return | Diagonal-tooth clutch engages during brake release for micro-adjustment | Mining equipment | Clutch slippage if oil-contaminated | |
| Hydraulic Piston | Brake fluid pressure moves piston; check valve locks position | Integrated caliper brakes | Seal degradation from fluid impurities | |
| Pneumatic Diaphragm | Air pressure deforms diaphragm to drive adjustment mechanism | Commercial vehicle air brakes | Diaphragm cracking in cold climates | |
| By Sensing Principle | Stroke-Triggered | Activates when pushrod travel exceeds set limit | Most road vehicles | False triggers from misalignment |
| Wear Accumulation | Mechanical counter initiates adjustment after preset brake cycles | Legacy systems | Under-compensation from miscounts | |
| Real-Time Feedback | Position sensors with ECU control | Electric/hybrid vehicles | Sensor corrosion in wet conditions | |
| By Configuration | Angular Drive (90°) | Worm gear transmits torque from perpendicular camshaft | S-cam drum brakes | Worm shaft binding due to abrasive wear |
| Coaxial Direct Drive | In-line force transmission with brake chamber | Disc brake integrations | Side-load induced bending fatigue | |
| Side-Mount Rocker | External rocker arm redirects motion vector | Compact excavators | Pivot joint seizure from mud ingress | |
| Specialized Variants | Arctic-Grade | Ice-resistant seals; low-temp lubricants; nickel-plated housing | Polar operations | Ice-jamming in refreeze cycles |
| Contamination-Proof | Sealed forged housing; oversized gear teeth | Off-highway dump trucks | Premature wear from silica abrasion | |
| Dual-Redundant Electro | Backup motor/sensor system with auto-failover | Rail transport | Electrical surge damage |